
Zhiqiao Guide: there are many factors affecting the forming, some of which are the factors affecting dehydration. Some factors are "congenital" to the forming process, such as the characteristics of fibers in pulp, the proportion of pulp, etc; Some factors are caused by the characteristics of the former, such as shaking, double-sided dehydration of the mesh clamp, etc; Some factors can be adjusted in the production process, such as pulp concentration, pulp net speed ratio, etc. Some common factors related to the above hydrodynamic processes will be discussed below.
1) Pulp concentration
Low pulp concentration can increase the mobility of fibers. When turbulence and shear disappear, the time required for fibers in low concentration pulp to form flocculent state is longer than that in high concentration pulp. For example, when the concentration is 1%, the flocculation time after the disturbance disappears is about 100 ms, when the concentration is 4%, it is only 1 ms, and when the concentration is 0.5%, it can reach about 500 ms. Therefore, low concentration is conducive to better dispersion of fibers.
When the shaper has enough dewatering capacity, papermakers are willing to use a lower pulp concentration in order to carry out the forming process under the condition of uniform fiber dispersion. For the production of low weight tissue paper and the use of some long fiber and sticky beating pulp, it is even more necessary to use a lower on-line concentration.
The dryness of wet web forming is usually 3 ~ 6%. If the concentration of pulp on the net is one tenth of this value, and considering that there is about 35% solid phase separation rate of pulp in the forming process, the amount of water to be removed in the forming process is about 93.5% of the water content of pulp on the net. This amount of dehydration is very large. Further reducing the pulp concentration will further increase the dewatered water, so it needs to be calculated or tested.
The decrease of pulp concentration also enhanced the activity of fine substances, and the loss of fine substances also increased when the initial discharge was fast. The net surface of the forming net is uneven, and the retention on and between the net lines is different, forming a net mark.
In the process of deposition, the higher the content of fine fibers and fine substances in the accumulation layer close to the net surface, the more the ups and downs of the accumulation layer close to the net surface can be close to each other, that is, the clearer the net mark reflected by the accumulation layer, and the net mark is strengthened. It can be seen from the above situation that when the concentration of pulp on the net is low, the chances of fine fibers and fine substances moving to the net surface increase, so the net mark also tends to increase.
2) Dehydration rate
The influence of dewatering speed on forming process and forming quality is multifaceted. The initial dewatering speed of pulp feeding is much different from that of the free suspension above the accumulation layer through the formed accumulation layer in the later stage of the forming process.
Dehydration rate is a variable value, which can be expressed theoretically by Kozeny Carman formula:
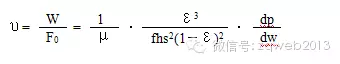
Hey, the formula is too complicated. Let's just say the result
When the initial dewatering speed is high, the defects in fiber distribution (if any) brought by the flow part will be quickly fixed, the loss of fiber and fine particles will increase, the mesh mark of wet paper web will be enhanced, and pinholes will be easy to be generated on the paper. These pinholes are the result of high-speed water flowing straight through the accumulation layer.
The high initial dehydration rate will also make the lower part of the accumulation layer compacted more firmly. It is difficult for the free suspension in the upper part of the accumulation layer to release water further. As a result, the later fiber deposition speed is reduced and the forming process time is relatively prolonged.
In addition to some thin paper, measures are usually taken to slow down the initial dehydration speed and make the dehydration at the initial stage of the forming process more gentle. Under the gentle initial dewatering speed, the directionality of the fiber arrangement at the lower part of the accumulation layer can be easily controlled, and the trend of the fiber arrangement perpendicular to the formed mesh surface can be reduced, which is conducive to the better dispersion of the fiber in the drainage.
3) Pulp net velocity difference
The pulp net velocity difference is a measure of directional shear. The speed difference between pulp and mesh is large, the longitudinal directional shear is also large, and the fibers are not arranged longitudinally, and the directionality is also strong. However, this directivity is weaker the farther away from the forming net from the net side of the accumulation layer.
The directional shear caused by the pulp net velocity difference also has a good effect on the dispersion of fibers in the free suspension without water discharge. The pulp speed is slightly faster or slower than the mesh speed, which reflects the improvement of fiber uniform distribution in the forming process. The influence of too large pulp mesh velocity difference on forming is bad. In most cases, the pulp net speed difference within ± 5% is adopted.
4) Forming net
Forming mesh is an essential component in the forming process. The dewatering of fiber suspension on the forming net is related to the effective flow area and mesh size of the forming net.
The effective flow area refers to the sum of all mesh areas in the unit formed mesh area, and the mesh size is the specific size of a single mesh. The effective circulation area is related to the mesh number and the diameter of the warp and weft lines. In a single woven net with less than 80 mesh per inch, the effective circulation area of the one with more mesh is usually less due to the increase of the warp and weft lines. When more than 80 meshes per inch, the effective circulation area usually increases with the increase of the number of meshes.
Under the same pressure difference and flow resistance, when the effective flow area is large, the dehydration speed is also high. When the effective flow area is the same and the mesh number is large, it indicates that the mesh size is small and the dehydration speed will be reduced due to the increase of flow resistance. Therefore, when the mesh is selected, that is, the forming mesh with small and dense mesh holes, more moderate dehydration can be obtained, and the fibers in the suspension have more opportunities to be evenly distributed in the deposition process, and there are more accumulation of fine fibers and fine substances.
5) Pulp temperature
The increase of pulp temperature can reduce the viscosity of water in the suspension and increase the dehydration rate. Fiber suspension is a three-phase suspension, because there will inevitably be more or less air in it.
Increasing the pulp temperature is conducive to the rapid escape of the gas phase in the suspension under the condition of rapid volume increase, so that the flow part or the attached degassing device has a better degassing effect. However, the increase of pulp temperature also creates favorable conditions for bacterial reproduction. It is easy to form mucinous rotten pulp in pulp and attach scale in pipes and machines, so as to reduce the quality of pulp or cause secondary waste products in paper. When the closed circulation system of white water under the net is adopted, the above problems caused by the increase of slurry temperature are more likely to occur.